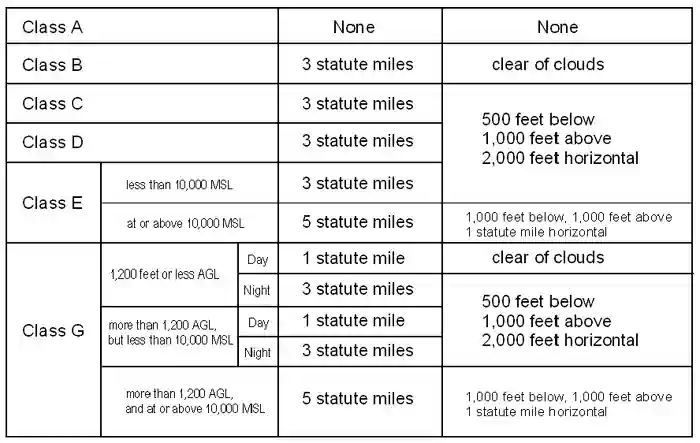
class g airspace visibility requirements
Understanding the rationale behind the different requirements might help you remember them more easily. 1200 or less above the surface regardless of MSL altitude Flight Visibility.

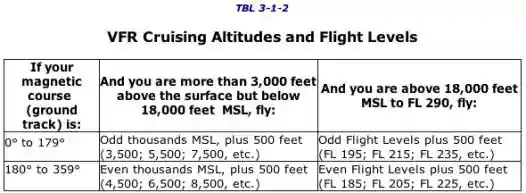
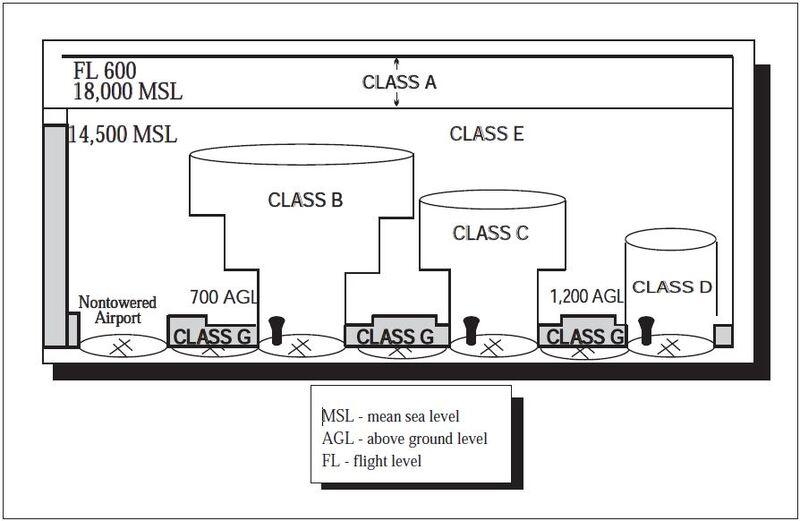
Airspace Visibility Requirements Diagram Quizlet
No person may operate an ultralight vehicle when the flight visibility or distance from clouds is less than that in the table found below.

. Airspace Requirements for Weather Minimums. Of airspace and altitudes. It surrounds the countrys busiest airports.
That is not otherwise designated Class B C or D airspace. Flight Rules Pilot Equipment. There are a few other limitations to be aware of in Class G airspace.
Daytime requirements for Class G are 1 statute mile visibility and clear of clouds to 1200ft. On the other hand Class G airspace has four different sets of altitude-dependent minimums. A Unless otherwise specified in the certificate holders operations specifications when conducting VFR helicopter.
And 1 SM horizontal of clouds AND must have 5 miles of visibility. FAA Regulations for Class G. 135609 VFR ceiling and visibility requirements for Class G airspace.
VFR flight is based on the principle of see and avoid. Class G airspace is the only form of uncontrolled airspace in the United States. 36 rows 2 If ground visibility is not reported at that airport unless flight visibility during landing or takeoff or while operating in the traffic pattern is at least 3 statute miles.
12 rows No person may operate an ultralight vehicle when the flight visibility or distance from clouds is less than that in the table found below. Daytime requirements for Class G are 1 statute mile visibility and clear of clouds to 1200ft. But it has some of.
Basic VFR Weather Minimums. All operations in Class A Class B Class C. Class B airspace has some of the most stringent equipment and communication requirements of any airspace.
For Class B C D and E airspace below an altitude of 10000 MSL the basic VFR weather. Flight visibility Distance from clouds. B No person may operate a helicopter under VFR in Class G airspace at an altitude of 1200 feet or less above the surface or within the lateral boundaries of the surface areas of Class B.
Class G minimum weather requirements exist so that you can see and avoid other aircraft. No person may operate an. And Class E is more restrictive than Class G airspace.
Class D airspace is more restrictive than Class E or Class G airspace. Class G airspace uncontrolled is that portion of airspace that has not been designated as Class A Class B Class C Class D or Class E airspace. Typically Class G airspace includes all of the airspace below 14500 ft.
Class C Airspace Class D Airspace Class E Airspace Class G Airspace. A Unless otherwise specified in the certificate holders operations specifications when conducting VFR helicopter. 135609 VFR ceiling and visibility requirements for Class G airspace.
All operations in Class A Class B Class C and Class. The only requirements are to have 1 mile of visibility and to stay clear of clouds.

Flying Ifr In Class G In Switzerland Permitted Now
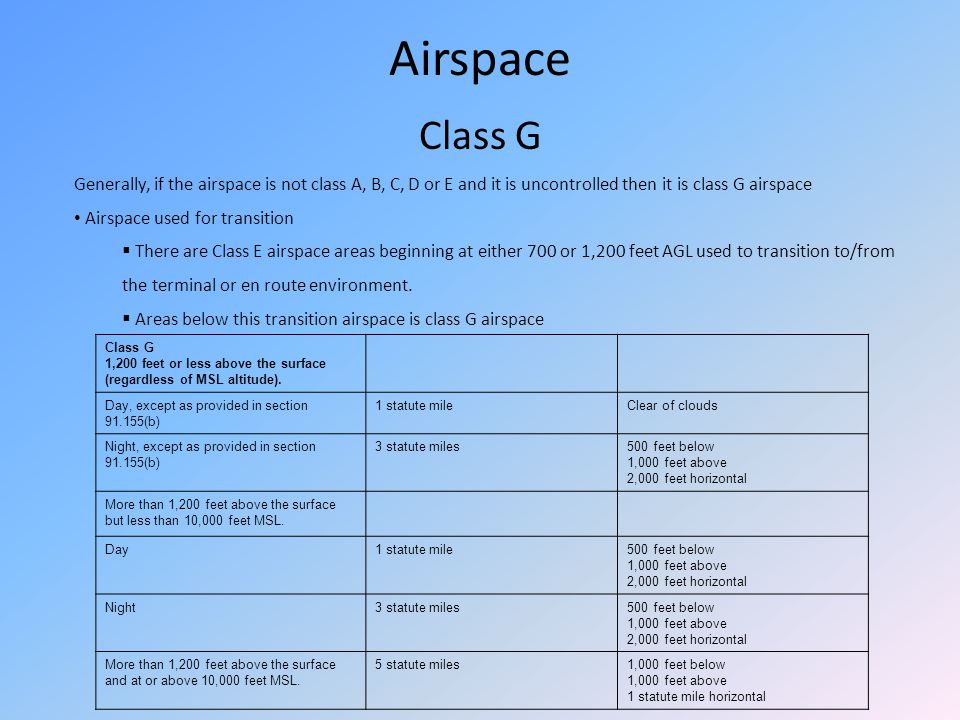
Atc And Ifr Procedures An Rco Creation Ppt Video Online Download

Vfr Unleashed Are We Allowed To Do That Aopa
Powered Parachute Flying Handbook Chapter 8 Airspace Classification And Requirements

Airspace Classes And Special Use Airspace Everything There Is To Know

Federal Register Helicopter Air Ambulance Commercial Helicopter And Part 91 Helicopter Operations

Helicopter Instrument Procedures Part Three
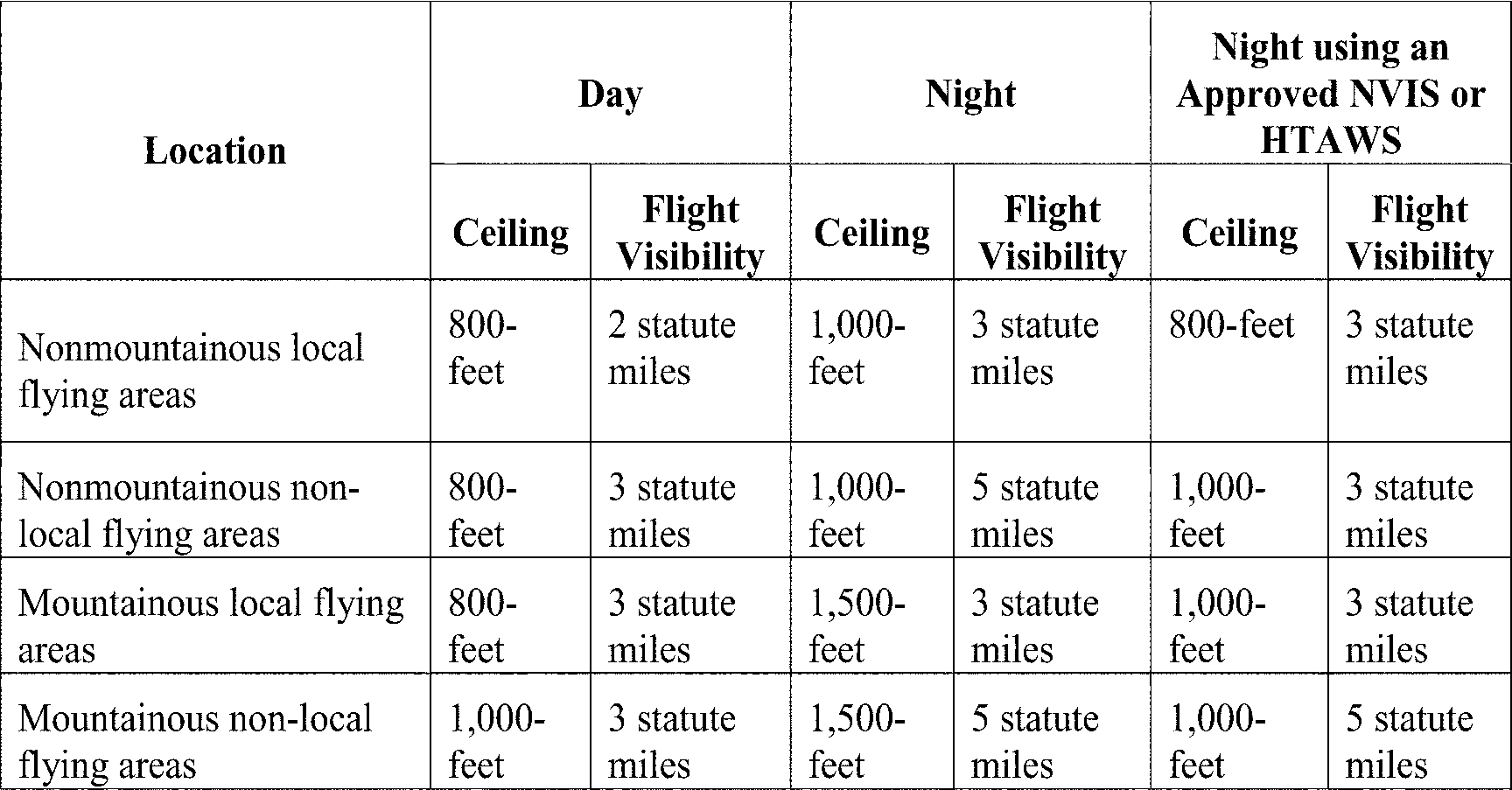
Far 135 609 Vfr Ceiling And Visibility Requirements For Class G Airspace Aviation Regulations
Enr 1 4 Ats Airspace Classification

Faa Airspace Card Pdf Visual Flight Rules Instrument Flight Rules

Private Pilot Airplane Lesson 4 3 14cfr Part 91 Faithful Guardian Aviation